レーザーシームステッパー
自動Cガン・ピッカー・ハンドヘルドシステム
IPGのCガン、ピッカー、ハンドヘルドシステムステッパーは、クランプとレーザー溶接ツール(最大4 kW)と組み合わせて、抵抗スポット溶接に代わるツールとして使用されます。最大3 kNまで調整可能なクランプ力、改良されたワークピースの強度と剛性、向上した加工速度や、費用のかかるレーザー安全キャビネットが不要といった特長があります。レーザーシームステッパーは、レーザーウォブルシームを最長40mmまで従来の半分のサイクルタイムで溶接し、熱成形材料など、さまざまな材料にも使用できます。オンラインモニタリング、ビームスイッチまたはインターロック電源安全システムを備えるCガンとピッカーレーザーシームステッパーは、クラス1*レーザー機器に適合します。
*インテグレーションにおいては、インターロックガードをマウントして、最小安全距離の1メートルを確保する必要があります。
Cガンレーザーシームステッパーは、クラス1レーザー機器に適合しています(インターロックガードによって、最小安全距離である1メートルを確保する必要があります)。LSS-2システムは、オンラインモニタリングとビームスイッチ安全システムを特長としています。コンパクトで効率的なステッパーヘッドの重量はわずか45 kgであり、圧縮空気を節約して、72 dB以下のノイズレベルで動作します。CガンLSSシステムは、最大2 kWのレーザー出力(統合チラーで制御)と最大4 kWのレーザー出力(スタンドアロンチラー)の2つの構成で提供されます。
機能
| シンプルなクランプテクノロジーを利用したレーザー溶接 | クラス1適合のレーザーシステム* |
| 最大出力4 kW | 電力変換効率 >30% |
| 短い加工時間 | 空冷式または水冷式 |
| マルチレイヤーシート接合により繰り返し加工可能 | コンパクト設計で一体化されたレーザーとCガン制御 |
| ジョイントの高強度と高剛性 | プログラムされたクランピングによる長期再現性 |
*インテグレーションには、インターロックガードをマウントして、最小安全距離である1メートルを確保する必要があります。
| 重量kg | 45 | |
| 調整可能なクランプ力(Zハブ)kN | 0.8-3.0 | |
| 長口幅Cガン mm | 130 | |
| 開溶接シーム mm | max. 40 | |
| ウォブル振幅(ウォブル) mm | ±1 | |
| 周波数(ウォブル周波数) Hz | 1-25 | |
| 接速度 mm/s | max. 50 | |
| 焦点距離 mm | 250 or 300 | |
| 圧縮空気の消費 l/min | 250 (作動中) | |
| 重量 kg | 400 | |
| 波長 | 1070 | |
| 動作モード | CW/ 変調 | |
| 公称出力 kW | max. 4 | |
| ビームスポットの直径 μm | 125, 250, 375, 500 | |
| 最大電力消費 kW | <14 (チラーなし) | |
| コントローラーサイズ (L x W x H) | 806 x 856 x 1517 | |
Cガンレーザーシームステッパーは、クラス1レーザー機器に適合しています(インターロックガードによって、最小安全距離である1メートルを確保する必要があります)。安全なLSS-5システムは、オンラインモニタリングとインターロック電源で構成されています。コンパクトで効率的なステッパーヘッドの重量はわずか45 kgであり、圧縮空気を節約して、72 dB以下のノイズレベルで動作します。LSS-5システムは、改良されたレーザーモジュールと電源を特長としており、電力変換効率は40%を超えています。CガンLSS-5は、最大2 kWのレーザー出力(内蔵チラーによって制御)と最大4 kWのレーザー出力(スタンドアロンチラー)の2つの構成で提供されます。
機能
| シンプルなクランプテクノロジーを利用したレーザー溶接 | 各溶接シームのリアルタイム溶接品質制御・データ記録 |
| 最大出力4 kW | 電力変換効率 >40% |
| マルチレイヤーシート接合によって繰り返し可能な加工 | チラー内蔵2 kWモデル |
| スマート溶接オプション | クラス1適合のレーザーシステム* |
| インターロック電源安全システム | |
*インテグレーションには、インターロックガードをマウントして、最小安全距離である1メートルを確保する必要があります。
| 2 kW | 4 kW | |
| 重量 kg | 45 | |
| 調整可能なクランプ力(Zハブ) kN | 0.8-3.0 | |
| 開口幅Cガン mm | 130 | |
| 溶接シーム長 mm | max. 40 | |
| ウォブル振幅(ウォブル) mm | ±1 | |
| 周波数(ウォブル周波数) Hz | 1-25 | |
| 溶接速度(mm/秒) mm/s | max. 50 | |
| 焦点距離 mm | 250 or 300 | |
| 圧縮空気の消費(l/分) l/min | 250 (作動中) | |
| 重量 kg | 200 | 400 |
| 波長 | 1070 | |
| 動作モード | CW/ 変調 | |
| 公称出力 kW | max. 2 | max. 4 |
| ビームスポットの直径 μm | 125 250 375 500 | |
| 最大電力消費 kW | <4.6 | <10.5 (チラーなし) |
| コントローラーサイズ(L x W x H) | 806 x 605 x 1479 | 806 x 856 x 1517 |
レーザーピッカーシームステッパーは、レーザー溶接ツールに片側からの固定動作を組み合わせたものです。LSS-2ヘッドは、1自由度で垂直なステージにマウントするか、数自由度でロボットにマウントすることができます。LSS-5レーザーピッカーのヘッドをロボットに装着すると、3D部品の溶接を柔軟に行うことができます。LSS-5は、改良されたレーザーモジュールと電源を特長としており、電力変換効率は40%を超え、コンパクトなヘッドの重量はわずか20 kgです。LSS-5は、最大2 kWのレーザー出力(内蔵チラーによって制御)と最大4 kWのレーザー出力(スタンドアロンチラー)の2つの構成で提供されます。
機能
| 加工対象に一方向から溶接可能 | プログラムされたフィクスチャリングによる長期再現性 |
| ステージまたはロボットへのマウント | ジョイントの高強度と高剛性 |
| 最大出力4 kW | コンパクト設計で一体化されたレーザーとCガン制御 |
| マルチレイヤーシート接合によって繰り返し可能な加工 | 短い加工時間 |
| 重量 kg | 40 | |
| 溶接シーム長 mm | max. 40 | |
| ウォブル振幅(ウォブル) mm | ±1 | |
| 周波数(ウォブル周波数) Hz | 1-25 | |
| 溶接速度mm/秒 | max. 50 | |
| 焦点距離 mm | 250 or 300 | |
| 圧縮空気の消費 l/分 | 250 (作動中) | |
| 重量 kg | 400 | |
| 波長 | 1070 | |
| 動作モード | CW/ 変調 | |
| 公称出力 kW | max.4 | |
| ビームスポットの直径 μm | 125, 250, 375, 500 | |
| 最大電力消費 kW | <14 (チラーなし) | |
| コントローラーサイズ (L x W x H) | 806 x 856 x 1517 | |
レーザーピッカーシームステッパーは、レーザー溶接ツールに片側からの固定動作を組み合わせたものです。LSS-2ヘッドは、1自由度で垂直なステージにマウントするか、数自由度でロボットにマウントすることができます。LSS-5レーザーピッカーのヘッドをロボットに装着すると、3D部品の溶接を柔軟に行うことができます。LSS-5は、改良されたレーザーモジュールと電源を特長としており、電力変換効率は40%を超え、コンパクトなヘッドの重量はわずか20 kgです。LSS-5は、最大2 kWのレーザー出力(内蔵チラーによって制御)と最大4 kWのレーザー出力(スタンドアロンチラー)の2つの構成で提供されます。
機能
| 加工対象に一方向から溶接可能 | スマート溶接オプション |
| ロボットへのマウント | 電力変換効率 >40% |
| 最大出力4 kW | チラー内蔵2 kWモデル |
| マルチレイヤーシート接合によって繰り返し可能な加工 | インターロック電源安全システム |
| 各溶接シームのリアルタイム溶接品質制御・データ記録 | |
| 2 kW | 4 kW | |
| 重量 kg | 20 | |
| 溶接シーム長 mm | max. 40 | |
| ウォブル振幅(ウォブル) mm | ±1 | |
| 周波数(ウォブル周波数)Hz | 1-25 | |
| 溶接速度 mm/s | max. 50 | |
| 焦点距離 mm | 250 or 300 | |
| 圧縮空気の消費 l/分 | 250 (作業中) | |
| 重量 kg | 200 | 400 |
| 波長 | 1070 | |
| 動作モード | CW/ 変調 | |
| 公称出力 kW | max. 2 | max.4 |
| ビームスポットの直径 μm | 125 250 375 500 | |
| 最大電力消費 kW | <5 | <14 (チラーなし) |
| コントローラーサイズ (L x W x H) | 804 x 605 x 1479 | 806 x 856 x 1517 |
IPGのLSS-3ハンドヘルドレーザーシームステッパーを使用して、溶接シームを手作業で作成することができます。頻繁にパラメータを変更し手動制御することが必要な、プロトタイプ、少量生産、車体修理などのアプリケーション用に設計されています。LSS-3シームステッパーはクランプとレーザー溶接ツールをコンパクトなヘッド内で組み合わせたもので、最大3 kNのクランプ動作と最大4 kWのレーザー出力を備えています。LSS-3はさまざまな材料で抵抗スポット溶接の後継として使用でき、調整可能なクランプ力、改良されたワークピースの強度と剛性、向上した加工速度、大幅に縮小されたフランジサイズ、最小の労力でのクランプなどの利点があります。LSS-3では、最長4 cmのレーザー溶接シームを作成できます。
機能
| 手動操作 | スマート溶接オプション |
| 最大出力4 kW | 電力変換効率 >30% |
| シンプルなクランプテクノロジーを利用したレーザー溶接 | クラス1適合のレーザーシステム* |
| 各溶接シームのリアルタイム溶接品質制御・データ記録 | コンパクト設計で一体化されたレーザーとCガン制御 |
*インテグレーションには、インターロックガードをマウントして、最小安全距離である1メートルを確保する必要があります。
| 重量 kg | 45 | |
| 調整可能なクランプ力(Zハブ) kN | 0.8-3.0 | |
| 開口幅Cガン mm | 130 | |
| 溶接シーム長 mm | max. 40 | |
| ウォブル振幅(ウォブル) mm | ±1 | |
| 周波数(ウォブル周波数) Hz | 1-25 | |
| 溶接速度 mm/s | max. 50 | |
| 焦点距離 mm | 250 or 300 | |
| 圧縮空気の消費 l/分 | 250 (作動中) | |
| 重量 kg | 400 | |
| 波長 | 1070 | |
| 動作モード | CW/ 変調 | |
| 公称出力 kW | max.4 | |
| ビームスポットの直径 μm | 125, 250, 375, 500 | |
| 最大電力消費 kW | <14 (チラーなし) | |
| コントローラーサイズ (L x W x H) | 806 x 856 x 1517 | |
アプリケーション
| 車体部品の溶接 | 軽薄材料の接合 |
| ハイグレードスチールやアルミニウムによる再現可能な溶接部 | 接合品質と部品剛性の向上 |
| 熱成形材料の安定した接合 | ひずみの小さい接合 |
| 高強度スチールの安定した溶接 | 少量生産のプロトタイプや部品の製造 |
Fiber Laser Seam Stepper Replacing Resistance Spot-Welding
A cost-effective laser based tool to conventional welding technologies
Andreas Siewert and Klaus Krastel, IPG Laser GmbH, Burbach, Germany
|
Resistance spot welding is known in high-volume production environment in the automotive industry since many years. The laser welding technology is also established in this application for more than 20 years, however it could still not capture the majority of the market even the modern laser welding application offers the following advantages:
|
One of the advantages for resistance spot welding (RSW) compared to laser welding is the integrated clamping technology, which comes nearly for free as well as the safety enclosure is not as complex, not consuming valuable space and therefore not as costly. The Laser-Seam-Stepper (LSS) from IPG Laser GmbH which has been developed in the last few years is designed to combine the advantages of a fast laserwelding process as well as the integrated clamping of the components. The new tool is integrated in a standard robot cell a Class 1 laser device, |
|
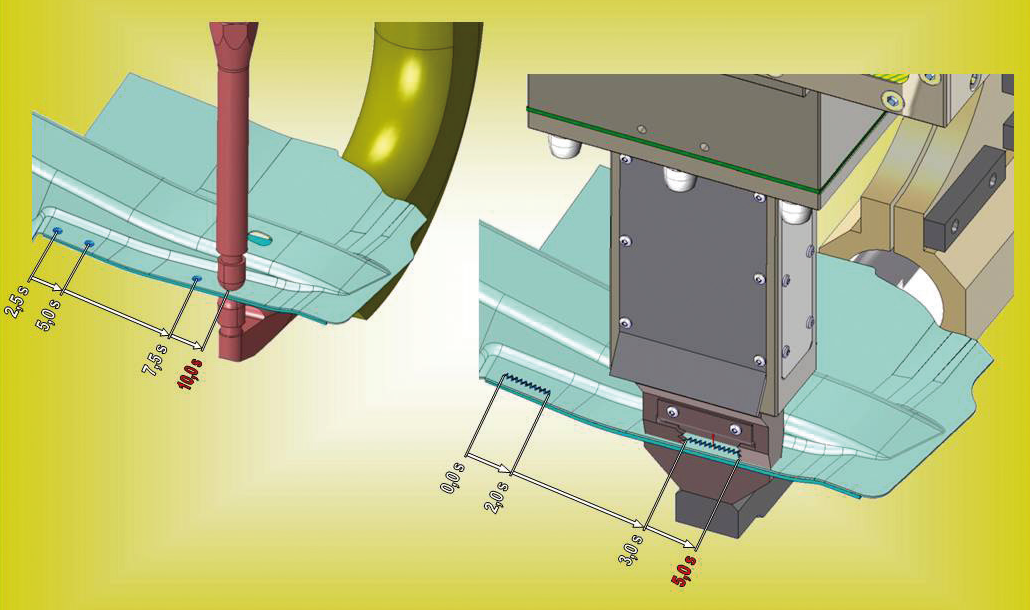
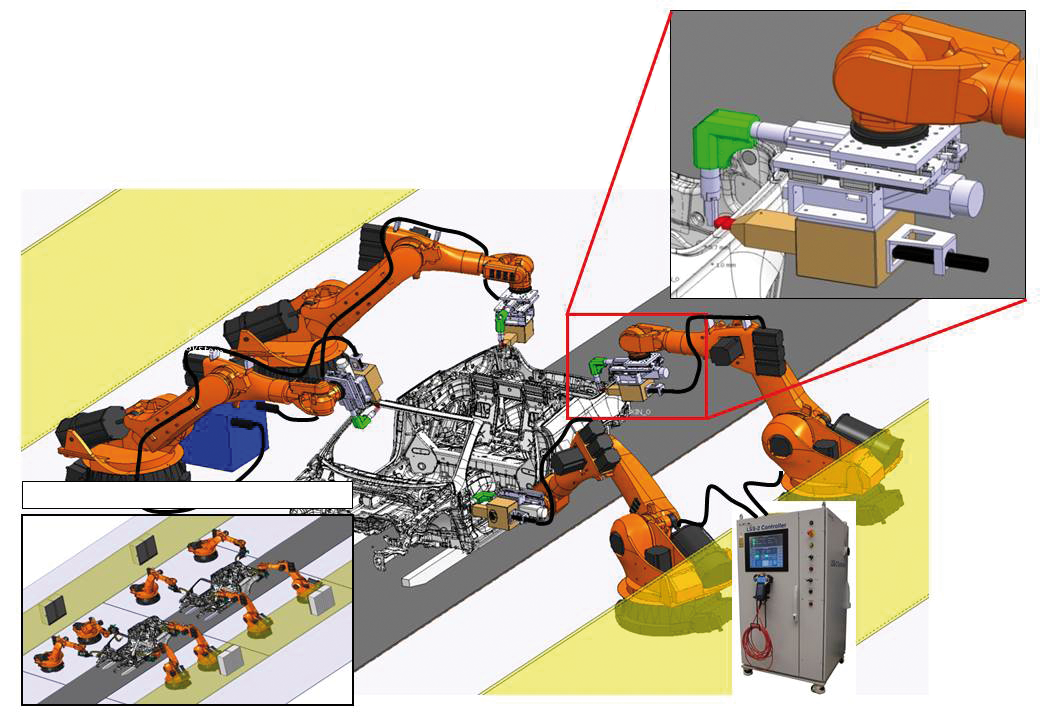
The concept of the Laser-Seam Stepper (LSS) is to have a maintenance free fiber laser combined with an easy clamping tool where the X-Y-movement is realized by the integrated welding head. To release the laser power, the housing has to contact the component to be welded which will guarantee the laser safety (Fig. 1). Laser welding with or without the weaving function (± 1 mm) can be effected within the range determined by the housing (standard = 40 mm). The easiest application is an LSS mounted, for example, on the sixth axis of an industrialrobot (with 50-kg handling capacity). The robot moves the LSS to the required welding position. In this position, it is placed onto the component only by robot force. Below the component, within the range of the welding seams, a fixed lower tooling is used as counter force or support (Fig. 1). |
 |
|
| Fig. 1 The Laser-Seam-Stepper is shown here with a “picker” (left) and a C-gun (right). |
|
|
During a typical stepping operation (30 mm welding seam, 30 mm of free space, 30 mm welding seam), a laser welding seam can be placed with a welding velocity of approximately 30 mm/s every 1.7 to 2.0 s (Fig. 2). The LSS unit is mounted on a servomotor-driven traversing unit. This is similar to a resistance-welding gun with a compensating module (Fig. 1). This version enables, for example, an industrial robot to move the module into a welding position and to close with a freely programmable force. The lower tool belonging to the C-gun (Fig. 1, right). is used as a counter force and additional safety equipment against unintendedback-reflected laser radiation. The force-controlled closing of the laser welding system (0.5 to 3 kN) results in a fitting accuracy (gap < 0.2 mm), which is deemed necessary for laser welding. The system’s compensation module compensates tolerances regarding the position and geometry of the components. All joining forces (0.5 to 3 kN) applied in the system are performed within the laser welding tool only; the robot itself is not required for these joining forces. During a typical stepping operation, a laser seam can be placed every 1.7 to 2.0 s. |
|
| Fig. 2 Resistance spot welding vs. laser welding with the LSS module. |
|
Typical applications for this system are sheet-metal assemblies in the body-in-white automotive production lines (Fig. 3), which until now have been joined with many resistance-welding spots. One laser seam step of approximately30 mm can replace two resistance-spot welds with a typical spacing of 30 mm. The cycle time for 30 resistance spot welds is approximately 75 s. If spot welding is replaced by laser seam welding in the prescribed manner, only 15 laser-weld seams are required. The cycle time can be reduced to a total of 37 s. Additional advantages are that the LSS requires less floor space and less capital investment cost in comparison to resistance spot welding. The Laser-Seam-Stepper basic version is designed to perform linear seam welds of up to 40 mm and in addition a weaving function with a preset frequency of 3–30 Hz can be switched on in order to spread the welding seam to 2 mm. |
 |
|
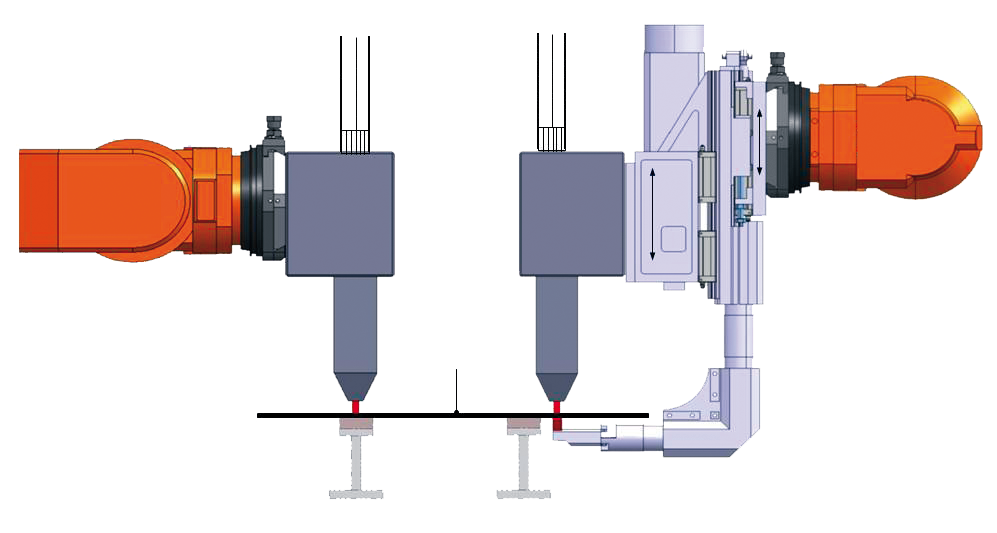
| Fig. 3 The LSS with fiber laser requires only one robot cell, whereas resistance spot welding would require two robot cells for the same operation. |
|
|
The overhaul running costs are reduced to a minimum by implementing unique features in the system. As the LSS is laser safe using standard robot welding cells there is no need of using complex and costly laser-protection housings. The system provides a clamping action to join sheet metal plates to be welded, with a defined force. This reduces the normally high requirements for additional clamping during standard laser welding as well as the maintenance of these components. A special designed air flow inside the LSS tool ensures the outperforming lifetime of the cover slide which protects the welding tool. The fiber laser and the LSS module are maintenance-free and the system is controlled via hardware interlock and standard bus systems. Preconfigured settings for length of weld (10 to 40 mm), speed, laser power, ramping, etc. can be selected which makes the programming of parts simple and easy. An optional available handheld LSS can be used for prototyping to produce laser welded parts within a short time without the need of using a robot. This offers OEM’s and suppliers a critical advantage in the form of time to market of parts and platforms. |
|
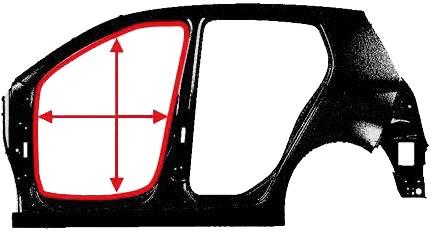
| Fig. 4 The module is tested during production of a triangle window at the door of a car. |
|
|
|
|
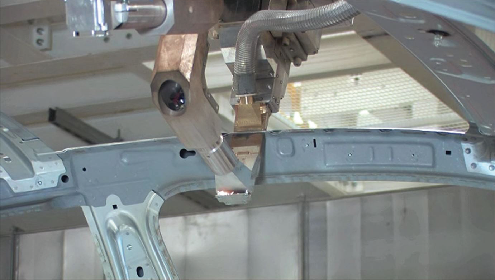
| Fig. 5 The module is tested during auto production; here, an interface B-pillar/rocker panel is being welded. | Fig. 6 The module is tested during production of a car roof frame. |
|
|
 |
|
| Fig. 7 Entry and weight optimization. | Fig. 8 Weight optimization. | |
|
With the experience of more than four years of production in a fully automated car plant the Laser-Seam-Steppers (LSS) is meanwhile used in various applications. The application is overlap welding with different material combinations. This can be zinc coated steel or high strength steel as well as stainless steel or aluminum (for example in the shipyard and rail wagon industries). The unique design of the upper and lower clamping brackets will allow to reduce the flanges from 15 mm (required for RSW) down to 10 mm or even 6 mm. |
This will allow
|
|
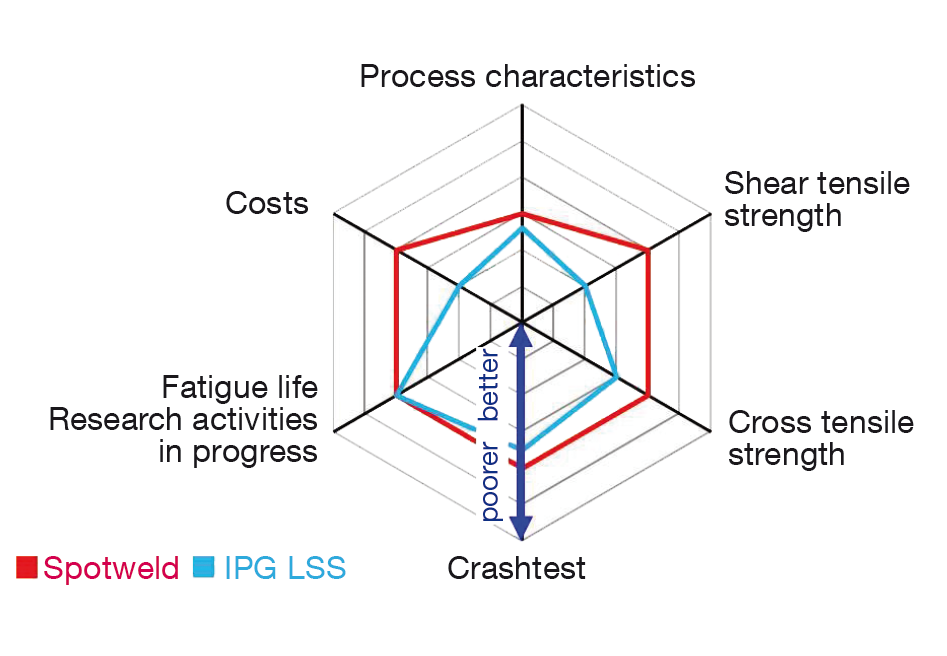
In cooperation with INPRO (an innovative company for advanced production systems in the automotive industry in Berlin; its cooperating partners are Daimler AG, Volkswagen AG, Siemens AG, ThyssenKrupp Technologies and SABIC Venture BV), the joining technology of resistance spot welding was compared with laser welding by the Laser-Seam-Stepper using a wobbled beam. Here, physical and technological features, behavior of the part itself and crash performance were taken into consideration, along with economic aspects. Fig. 9 illustrates the overall evaluation of the considered factors for laser welding by LSS (blue line) and resistance spot welding (red line). The line nearer to the middle for laser welding represents a better result than the one achieved by resistance spot welding. The overall technical result shows that the performance of the wobbled seam produced by the new welding module is comparable to or even better than resistance spot welding and can complete welding tasks in half the production time. The result of economic comparison shows a total cost reduction of 6 to 10 percent, assuming fully automated production of 800 units in three-shift operation. |
 |
|
| Fig. 9 Overall evaluation of the process comparison. |